
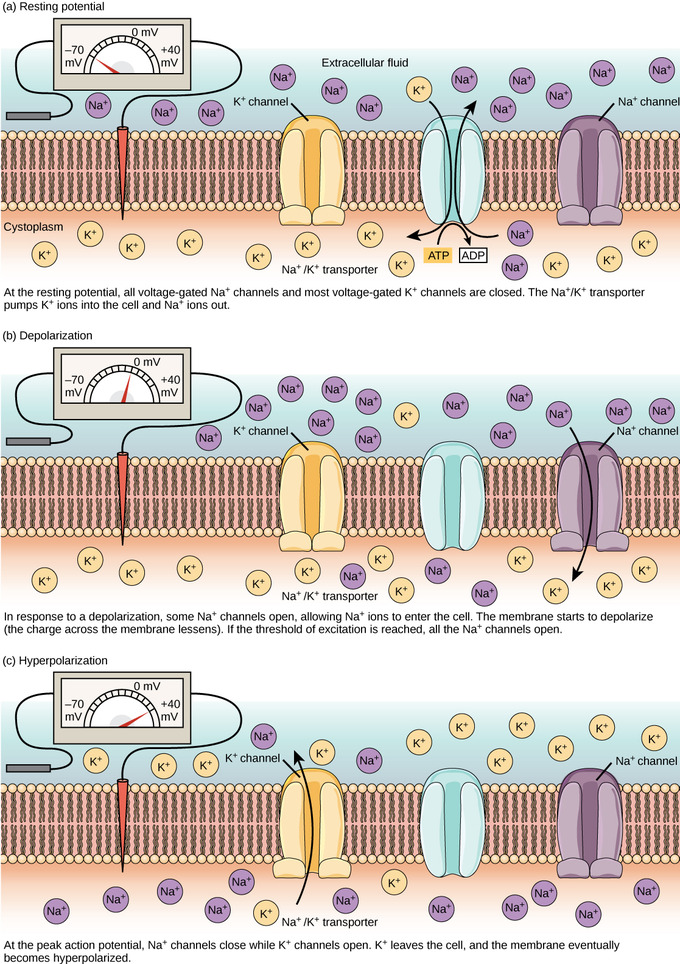
‘personal data’ means any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person (‘data subject’) an identifiable natural person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identifier such as a name, an identification number, location data, an online identifier or to one or more factors specific to the physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural or social identity of that natural person. If a depolarizing graded potential is sufficiently large, Na + channels in the trigger zone open. Action potential. Unlike a graded potential, an action potential is capable of traveling long distances. The following four steps describe the initiation of an impulse to the “resetting” of a neuron to prepare for a second stimulation: Light, heat, mechanical pressure, and chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, are examples of stimuli that may generate a graded potential (depending upon the neuron).įigure 1.Events that characterize the transmission of a nerve impulse. Graded potentials occur in cell bodies and dendrites. A graded potential is a local event that does not travel far from its origin. If the stimulus opens K + channels, then positive potassium ions exit across the membrane and the membrane hyperpolarizes (becomes more negative). If Na + channels open, positive sodium ions enter, and the membrane depolarizes (becomes more positive). A graded potential occurs when the stimulus causes Na + or K + gated channels to open. Graded potential. A graded potential is a change in the resting potential of the plasma membrane in the response to a stimulus. Resting potential. The resting potential describes the unstimulated, polarized state of a neuron (at about –70 millivolts). The following events characterize the transmission of a nerve impulse (see Figure 1): In addition to crossing the membrane through leakage channels, ions may cross through gated channels. Gated channels open in response to neurotransmitters, changes in membrane potential, or other stimuli. It is these large, negatively charged ions that contribute to the overall negative charge on the inside of the cell membrane as compared to the outside. Other ions, such as large, negatively charged proteins and nucleic acids, reside within the cell. The resting membrane is much more permeable to potassium ions than to sodium ions resulting in slightly more net potassium ion diffusion (from the inside of the neuron to the outside) than sodium ion diffusion (from the outside of the neuron to the inside) causing the slight difference in polarity right along the membrane of the axon. The main contribution to the resting membrane potential (a polarized nerve) is the difference in permeability of the resting membrane to potassium ions versus sodium ions. A certain amount of Na + and K + is always leaking across the membrane through leakage channels, but Na +/K + pumps in the membrane actively restore the ions to the appropriate side. 
Polarization is established by maintaining an excess of sodium ions (Na +) on the outside and an excess of potassium ions (K +) on the inside. The inside is negative with respect to the outside. The membrane of an unstimulated neuron is polarized-that is, there is a difference in electrical charge between the outside and inside of the membrane. The transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron from one end to the other occurs as a result of electrical changes across the membrane of the neuron.

Quiz: Regulation of Urine Concentration.Quiz: Structure of the Digestive Tract Wall.Quiz: Function of the Respiratory System.Quiz: Structure of the Respiratory System.Quiz: Supplements to the Immune Response.Quiz: Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immune Responses.Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immune Responses.Quiz: Specific Defense (The Immune System).The Immune System and Other Body Defenses.Quiz: Functions of the Cardiovascular System.Quiz: The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Glands.
Quiz: The Ventricles and Cerebrospinal Fluid.Quiz: Muscle Size and Arrangement of Muscle Fascicles.Muscle Size and Arrangement of Muscle Fascicles.Quiz: Structure of Cardiac and Smooth Muscle.Quiz: Connective Tissue Associated with Muscle Tissue.Connective Tissue Associated with Muscle Tissue.Quiz: Chemical Reactions in Metabolic Processes.Chemical Reactions in Metabolic Processes.Quiz: Atoms, Molecules, Ions, and Bonds.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
