
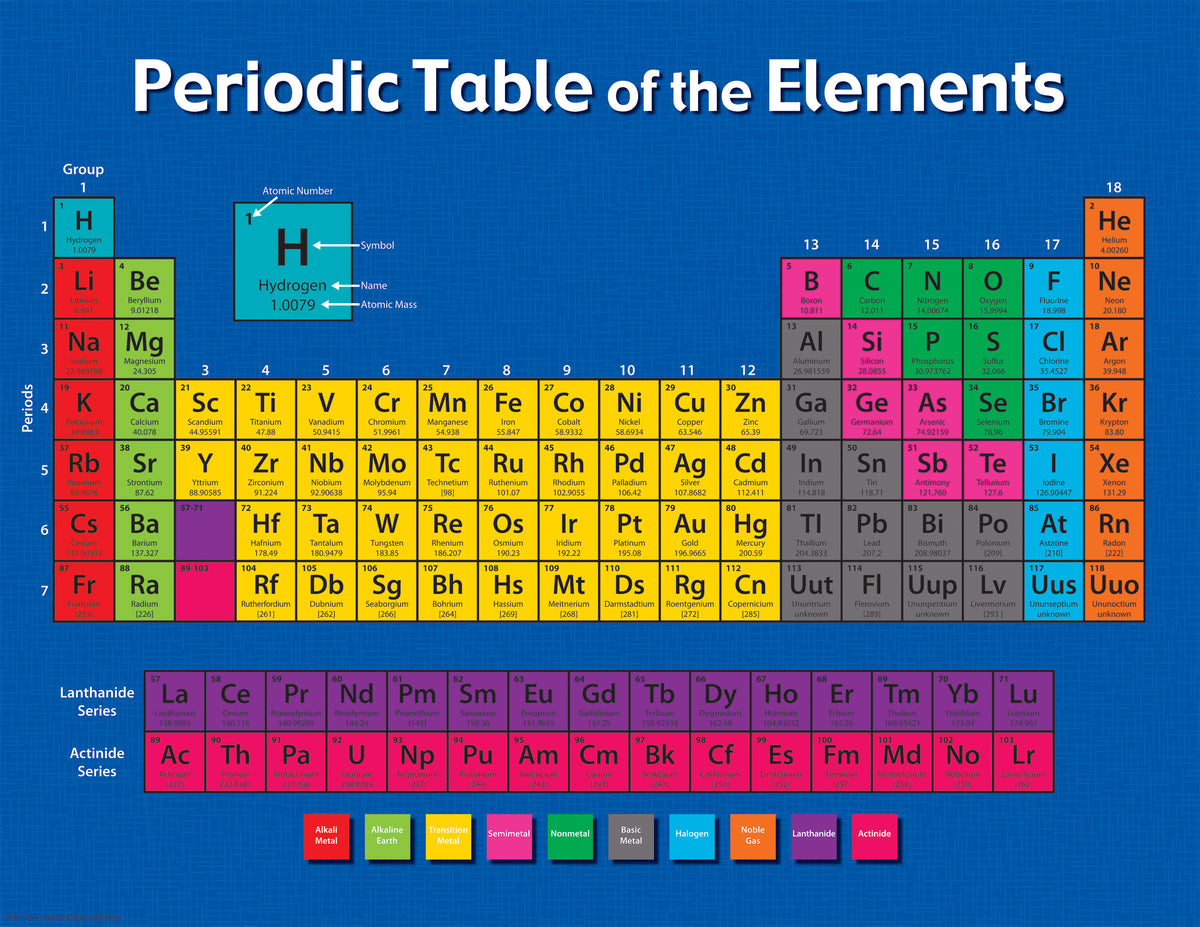
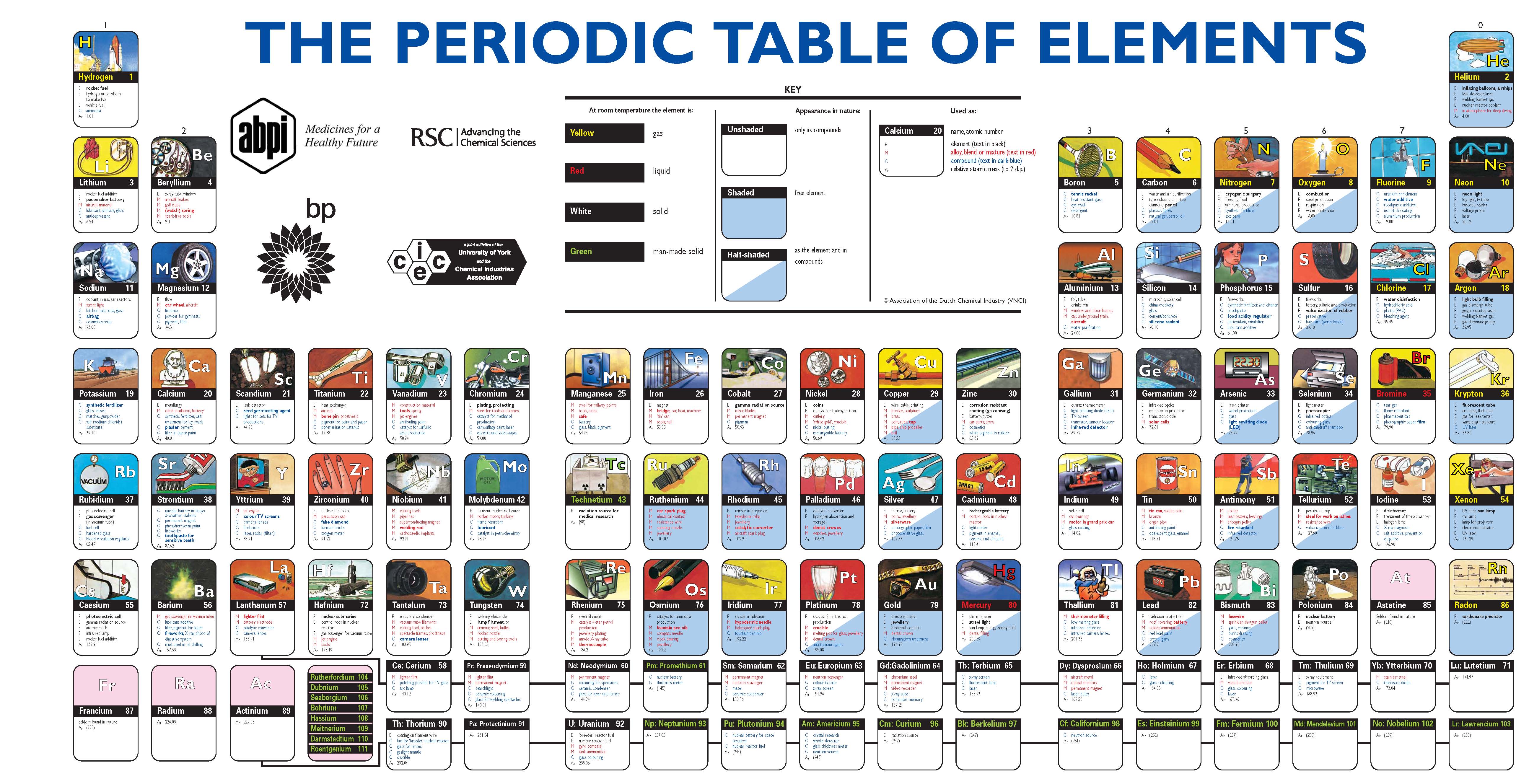
In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. See also: Atomic Number – Does it conserve in a nuclear reaction? Atomic Number and Chemical PropertiesĮvery solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. It is the electrons that are responsible for the chemical bavavior of atoms, and which identify the various chemical elements. In a neutral atom there are as many electrons as protons moving about nucleus. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10 -19 coulombs. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. K) 11.3 Thermal Conductivity 200 Specific Heat 1.82 Heat of Fusion 12.2 Heat of Vaporization 292.4 Atomic Number of Beryllium.it emits photoneutrons).īeryllium – Properties Element Beryllium Atomic Number 4 Symbol Be Element Category Alkaline Earth Metal Phase at STP Solid Atomic Mass 9.0122 Density at STP 1.848 Electron Configuration 2s2 Possible Oxidation States +1 +2 Electron Affinity - Electronegativity 1.57 1st Ionization Energy 9.3226 Year of Discovery 1797 Discoverer Vauquelin, Nicholas Louis Thermal properties Melting Point 1278 Boiling Point 2469 Thermal Expansion µm/(m The Sb-Be source is based on (γ,n) reaction (i.e.
Since berylium has very low threshold energy for neutron emission, it can be used as a neutron source in nuclear reactors. Therefore, it works as a neutron reflector and neutron moderator, effectively slowing the neutrons to the thermal energy.
Beryllium has a large scattering cross section for high-energy neutrons, about 6 barns for energies above approximately 10 keV. The commercial use of beryllium requires the use of appropriate dust control equipment and industrial controls at all times because of the toxicity of inhaled beryllium-containing dusts that can cause a chronic life-threatening allergic disease in some people called berylliosis. The chemical symbol for Beryllium is Be.īeryllium is a hard, grayish metal naturally found in mineral rocks, coal, soil, and volcanic dust. Beryllium is a chemical element with atomic number 4 which means there are 4 protons and 4 electrons in the atomic structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
